 |
 |
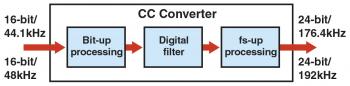
| CC Converter |
|
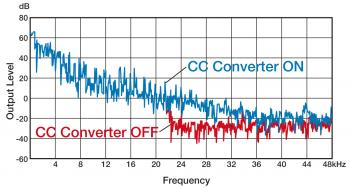
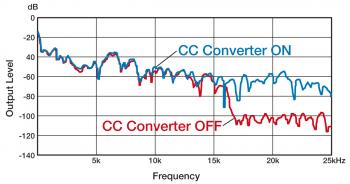
When an analog signal is converted into digital (A/D conversion), high frequencies -- normally those higher than 20kHz with CDs -- are removed as dictated by the CD's sampling frequency. Absence of this high-frequency data affects the quality of sound in the audible range.
The CC Converter (Compression Compensative Converter) features exclusive algorithms to restore lost signals based on the recorded digital signals of audible frequencies, those frequencies that should have been recorded in the first place. It also uses high-bit quantization to reproduce minute signals. Moreover, in order to precisely reproduce the signals that have undergone such processing, the CC Converter features a broader analog bandwidth (up to 4 times the sampling frequency) extending beyond 20kHz. This improves the quality of the music data in the audible range.
Through high-bit/high-sampling processing, the CC Converter generates expanded digital signals with a quality close to that of the original master.
The algorithms of the CC Converter have been verified for their musical legitimacy by studio engineers and musicians through repeated auditions. Because the number of digital sound sources has been growing fast, the CC Converter has proved to be a much-sought-after solution for the faithful recreation of original sound. It also works with compressed data, such as Dolby Digital and DTS formats.
(RX-D702/RX-D302/RX-D301)
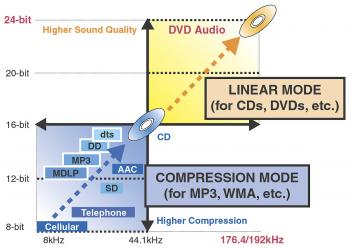
In response to the growing popularity of PC music files, JVC has upgraded the CC Converter so it applies different algorithms for non-compressed hi-fi (CDs, DVDs and other linear formats) and compressed audio (MP3, WMA, and others). Compressed music has never sounded better or clearer. |
|
|
 |

